Physical Security
Physical Security is all the security measures and methods that are taken to secure a place from external attacks or actions from unauthorised people that can cause damage to a system or a business. This damage could be fire, burglary, theft, vandalism, etc. There are plenty of methods that can protect a system or a business from these attacks, such as:
- Locks
- Visitors Passes
- Sign In/Out Systems
- Biometrics
- Security
Locks
Locks are useful tools that can improve the security of a system – door and only the authorised personnel can have keys for access in certain areas, but locks are not the best tool to secure valuable and precious information because it’s easy to break them.

Visitors Passes
Visitors Passes is another method to keep secure a system or a business. Visitor Passes are cards that are authorised to gain access to certain areas. These passes should be given only on authorised people that are trustworthy.

Sign In/Out Systems
Sign In/Out Systems are software that allows users/visitors to gain access to an area that only authorised people should have access to. This software works with accounts, so if you want to enter an area or a system you have to sign in with your authorised account. For example in our college, only the tutors have access to software such as Pro-monitor, and they can control our grades.

Biometrics
Biometrics is a very useful and hard-to-hack method to improve the security of a system. Biometrics could be many different measures such as:
- Retinal Scans
- Fingerprint Sensors
- Voice Recognition
Retinal Scans
Retinal Scans are a very smart way to improve the security of a system/area and in my opinion, is one of the hardest methods for someone to hack into. Retinal Scan is a biometric technique that scans your eye and uses data from your eye so if you are authorised you can have access to areas that only authorised people can go to.

Fingerprint Sensors
Fingerprint Sensors is another biometric technique to keep secure a system. A fingerprint scanner is a type of technology that identifies and authenticates the fingerprints of an individual in order to grant or deny access to a computer system or a physical facility.

Voice recognition
Voice or speaker recognition is the ability of a machine or program to receive and interpret dictation or to understand and carry out spoken commands. Voice recognition has gained prominence and uses with the rise of AI and intelligent assistants, such as Amazon’s Alexa, Apple’s Siri and Microsoft’s Cortana

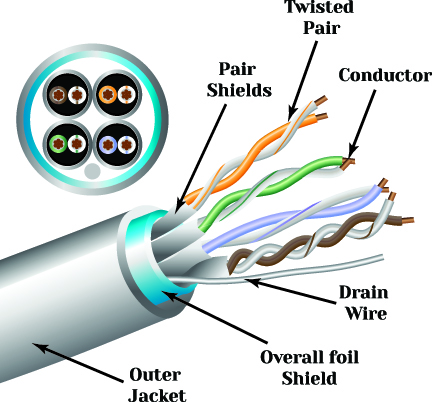
Cable Shielding
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) is prevalent throughout the factory floor. This is why data and signal cables are usually protected with insulated conductors and wrapped with a conductive layer. Shielding reduces electrical noise and reduces its impact on signals and also lowers electromagnetic radiation.
Guards
Guards are another method that a business can use to keep secure restricted areas. The Guards should keep secure a place and give access to enter restricted areas only to authorised people.

Software and Network Security
Encryption
Encryption is the method by which information is converted into a secret code that hides the information’s true meaning in such a way that only authorised parties can access it and those who are not authorised cannot.

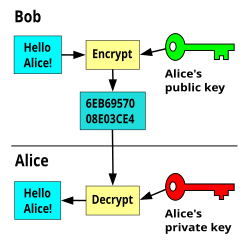
Public and Private Key Cryptography
In public-key cryptography, two keys are used, one key is used for encryption and while the other is used for decryption. In private key cryptography, the key is kept as a secret. In public-key cryptography, one of the two keys is kept as a secret.
Call Back
Callback is a piece of executable code that is passed as an argument to other code, which is expected to call back (execute) the argument at some convenient time. With this technique, a business can give access to authorised people so they can have access to restricted information or systems.
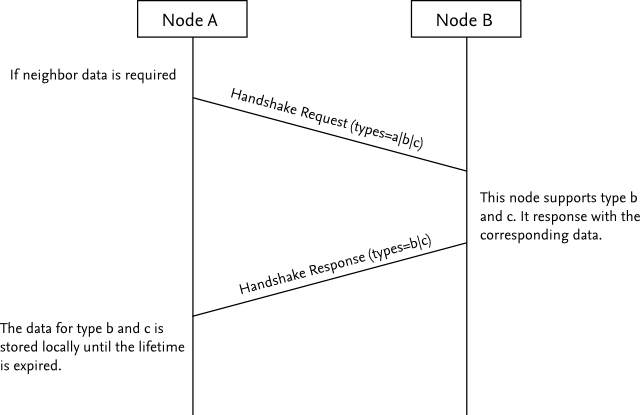
Handshaking
The handshake is often the steps of verifying the connection between the speed or the authorisation of the computer trying to connect to it. An example of handshaking is when a modem connects to another Modem; the tones heard after the dialing is the handshake and is how the computers greeting each other.
Diskless Network
A diskless network is a group of workstations that have no individual hard-drives and relies on a network boot from the server to boot an operating system on to each workstation. As each workstations OS is booted and managed from the connected network, every file is stored on the network and is shared between them.

Backups
Regular backups are very important in a system. Regular backup is a type of prevention in a case of a cyber-attack, software of media faults, viruses or hacking. Security needs to be considered for all copies of your data, including your working data set, backup copies and archived copies. For example if some hack into a system and delete data from the database, a backup can restore all the lost information.

Audit Logs
Audit Logs is a security chronological record that shows evidence of all the actions that have affected at any time a specific operation, procedure, or event. Audit Logs can be used to identify any actions that occur damage or change data on databases or systems. For example, if someone hacks into a database and changes the data you can see from the audit logs the changes and you can restore the data easier.
Firewall Configuration
A Firewall is very important for a business and helps to prevent any cyber-attacks. A firewall is a system designed to prevent unauthorized access to or from a private network. You can implement a firewall in either hardware or software form, or a combination of both. Firewalls prevent unauthorized Internet users from accessing private networks connected to the internet, especially intranets.

Virus Checking Software
Virus Checking Software (Antivirus Software) is a type of program designed and developed to protect computers from malware like viruses, computer worms, spyware, botnets, rootkits, keyloggers and such. Antivirus programs function to scan, detect and remove viruses from your computer. Every business should do scans for viruses, spyware, worms every week to prevent loss of data.

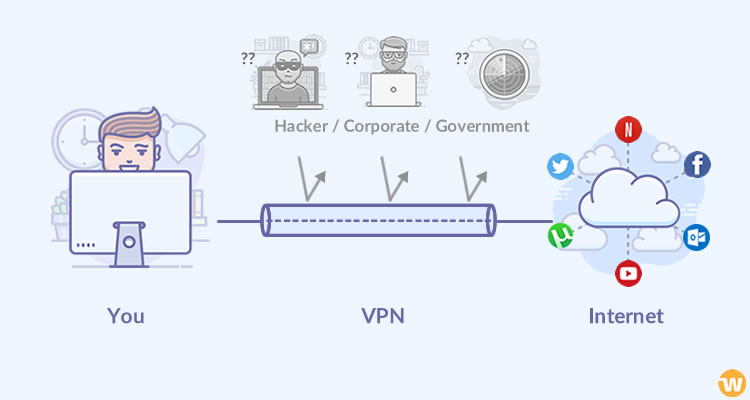
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
A VPN is very important for businesses that work with valuable information. A VPN is a private network that uses a public network (usually the internet) to connect remote sites or users together. The VPN uses “virtual” connections routed through the internet from the business’s private network or a third-party VPN service to the remote site or person.
Intruder Detection System
An intrusion detection system (IDS) is a device or software that monitors network traffic for suspicious activity and issues alerts when such activity is discovered. Any malicious activity or violation is typically reported either to an administrator or collected centrally using a security information and event management system.

Passwords
Passwords are very important for the security of a system. Passwords are the most important measurement for the security and the safety of a system, so if a password is very strong and difficult to hack the system is better protected. For a password to be powerful and strong should have the following criteria:
- A strong password consists of at least 8 characters (and the more characters, the stronger the password)
- The characters should be a combination of letters, numbers and symbols (@, #, $, %, etc.)
- A mixture of both uppercase and lowercase letters.


Levels of Access
In a company, there are some administrators and moderators that are responsible to regulate the company’s website, databases and make important changes for the company. This level of access is important to be given to trustworthy people because anyone with a high level of access can cause serious damage to a company and some times this damage can be irreversible.
Software Updating
Software updating is very important for the security of a system. Sometimes people who wants to break the security of a system(hackers) invent new methods to do it, so a system must be always up to date to defend every possible attack.
Backup System
Every business should have backup of their data such us payments, clients information and details etc., so if a disaster happens such as a fire, or an earthquake the business will have a backup of this information to restore.

Tiers of Recovery
There are 7 different Tiers of recovery. Depending on which tier the business is, it is changing the costs and the possibilities of recovery in a disaster or loss of data situation.
- Tier 0: No off-site data.
- Tier 1: Data backup with no hot site.
- Tier 2: Data backup with a host site.
- Tier 3: Electronic vaulting.
- Tier 4: Point-in-time copies.
- Tier 5: Transaction integrity.
- Tier 6: Zero or near-Zero data loss.
- Tier 7: Highly Automated, business integrated solution
Tier 0: No off-site data
Businesses with a Tier 0 business continuity solution have no Business Continuity Plan. There is no saved information, no documentation, no backup hardware, and no contingency plan. The time necessary to recover in this instance is unpredictable. In fact, it may not be possible to recover at all.
Tier 1: Data backup with no hot site</h3>
Businesses that use Tier 1 continuity solutions back up their data and send these backups to an off-site storage facility. The method of transporting these backups is often referred to as “PTAM” – the “Pick-up Truck Access Method.” Depending on how often backups are created and shipped, these organizations must be prepared to accept several days to weeks of data loss, but their backups are secure off-site. However, this tier lacks the systems on which to restore data.
Tier 2: Data backup with a hot site
Businesses using Tier 2 business continuity solutions make regular backups on tape. This is combined with an off-site facility and infrastructure (known as a hot site) in which to restore systems from those tapes in the event of a disaster. This solution will still result in the need to recreate several hours or even days worth of data, but the recovery time is more predictable.
Tier 3: Electronic vaulting
Tier 3 solutions build on the components of Tier 2. Additionally, some mission critical data is electronically vaulted. This electronically vaulted data is typically more current than that which is shipped via PTAM. As a result there is less data recreation or loss after a disaster occurs.
The facilities for providing Electronic Remote Vaulting consists of high-speed communication circuits, some form of channel extension equipment and either physical or virtual Tape devices and an automated tape library at the remote site. IBM’s Peer-to-Peer VTS and Sun’s VSM Clustering are two examples of this type implementation.
Tier 4: Point-in-time copies
Tier 4 solutions are used by businesses that require both greater data currency and faster recovery than users of lower tiers. Rather than relying largely on shipping tape, as is common on the lower tiers, Tier 4 solutions begin to incorporate more disk based solutions. Several hours of data loss is still possible, but it is easier to make such point-in-time (PiT) copies with greater frequency than tape backups even when electronically vaulted.
Tier 5: Transaction integrity
Tier 5 solutions are used by businesses with a requirement for consistency of data between the production and recovery data centers. There is little to no data loss in such solutions, however, the presence of this functionality is entirely dependent on the application in use.
Tier 6: Zero or near-Zero data loss
Tier 6 business continuity solutions maintain the highest levels of data currency. They are used by businesses with little or no tolerance for data loss and who need to restore data to applications rapidly. These solutions have no dependence on the applications or applications staffs to provide data consistency.
Tier 6 solutions require some form of Disk Mirroring. There are various synchronous and asynchronous solutions available from the mainframe storage vendors. Each solution is somewhat different, offering different capabilities and providing different Recovery Point and Recovery Time objectives.
Often some form of automated tape solution is also required. However, this can vary somewhat depending on the amount and type of data residing on tape.
Tier 7: Highly automated, business integrated solution
Tier 7 solutions include all the major components being used for a Tier 6 solution with the additional integration of automation. This allows a Tier 7 solution to ensure consistency of data above that which is granted by Tier 6 solutions. Additionally, recovery of the applications is automated, allowing for restoration of systems and applications much faster and more reliably than would be possible through manual business continuity procedures.
Explain the operation and use of an encryption technique in ensuring the security of transmitted information
SOURCES:
https://searchsecurity.techtarget.com/definition/physical-security
http://www.fleminc.com/newsblog/5/how-does-retinal-scanning-work
https://www.techopedia.com/definition/29808/fingerprint-scanner
https://searchcustomerexperience.techtarget.com/definition/voice-recognition-speaker-recognition
https://searchsecurity.techtarget.com/definition/encryption
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-between-private-key-and-public-key/https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-between-private-key-and-public-key/
https://www.codefellows.org/blog/what-is-a-callback-anyway/
https://computer.howstuffworks.com/vpn.htm
https://searchsecurity.techtarget.com/definition/intrusion-detection-system
https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/h/handshak.htm